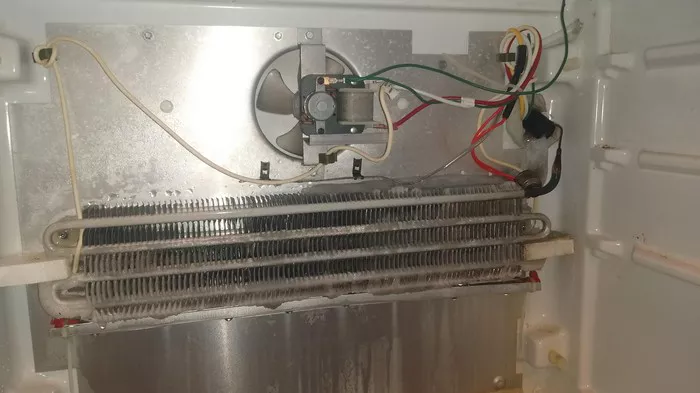
The evaporator fan is a critical component in refrigeration systems, HVAC units, and many cooling appliances. Whether in a home refrigerator, a commercial freezer, or an industrial air conditioning system, the evaporator fan plays a vital role in ensuring efficient cooling. This article provides an in-depth look at how an evaporator fan works, including its function, design, importance, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
What is an Evaporator Fan?
An evaporator fan is a fan typically located inside the evaporator coil section of a refrigeration or air conditioning system. It is responsible for circulating the air over the evaporator coils, which contain a refrigerant that absorbs heat from the air inside a room or compartment. By moving air across these coils, the fan facilitates the heat exchange process, which leads to cooling.
The fan ensures that the refrigerant within the coils effectively absorbs heat from the surrounding air, making the system more efficient. Without the evaporator fan, air circulation would be minimal, leading to inefficient heat transfer and poor cooling performance.
The Role of the Evaporator Fan in a Refrigeration System
In refrigeration systems, the process of cooling involves a continuous loop of heat transfer. The evaporator fan aids in this process by circulating warm air over the evaporator coils. Here’s how it works:
Heat Absorption: As warm air from inside the refrigerator or room is drawn into the evaporator coils, the refrigerant inside the coils absorbs the heat.
Air Circulation: The evaporator fan pushes the air over the coils and into the cooled space. This ensures that the air remains at a constant temperature, and the cooling process continues effectively.
Even Distribution of Cool Air: The fan helps distribute cool air evenly throughout the space, whether in a refrigerator, freezer, or air-conditioned room, preventing hotspots where the air would remain warmer than desired.
In summary, the fan facilitates the heat exchange process by maintaining airflow over the evaporator coils, allowing the refrigerant to absorb and carry away the heat from the air.
Components of an Evaporator Fan
To understand how the evaporator fan works, it’s essential to know the main components of this system:
Evaporator Coils: The evaporator coils are filled with refrigerant and are responsible for absorbing heat from the air.
Fan Motor: The fan motor is the power source that drives the evaporator fan blades. It is typically powered by electricity and can either be a direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) motor, depending on the design of the system.
Fan Blades: The blades are attached to the motor and help circulate the air over the evaporator coils. These blades are designed to create airflow efficiently and quietly.
Fan Housing: The housing contains the fan blades and motor, preventing the components from coming into contact with other parts of the system. It also helps channel the airflow in the desired direction.
Thermostat or Temperature Sensor: A thermostat or temperature sensor in the system often monitors the temperature inside the environment. This helps control the operation of the evaporator fan, ensuring that it works in sync with the cooling process.
How the Evaporator Fan Works in a Cooling Cycle
The evaporator fan plays a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle. Let’s break down how it works within the context of this cycle:
The Refrigeration Cycle: An Overview
The refrigeration cycle consists of four main stages:
Compression: The compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, turning it into a gas.
Condensation: The hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas is then cooled in the condenser coils, where it condenses into a high-pressure liquid.
Expansion: The high-pressure liquid refrigerant moves through an expansion valve, where it loses pressure and temperature.
Evaporation: The low-pressure refrigerant enters the evaporator coils, where it absorbs heat from the air, evaporates, and turns into a gas once again.
The Evaporator Fan in Action
As the refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator coils, the temperature of the surrounding air drops. Here’s where the evaporator fan’s role becomes crucial:
The fan is powered by the fan motor, which pulls air from the surrounding space (e.g., inside a refrigerator or room) and pushes it over the evaporator coils.
As the air passes over the coils, it loses heat, which is absorbed by the refrigerant. The now-cooled air is then blown back into the environment, ensuring a consistent and even temperature.
The fan continues circulating the air until the thermostat or temperature sensor detects that the space has reached the desired temperature. At this point, the fan may slow down or stop depending on the system design.
This process repeats in a continuous cycle to maintain the optimal temperature of the space being cooled.
Importance of the Evaporator Fan in Cooling Efficiency
The efficiency of the evaporator fan directly impacts the overall performance of the cooling system. Here are some key reasons why the evaporator fan is vital to efficient cooling:
Enhanced Heat Transfer: By ensuring consistent airflow across the evaporator coils, the fan allows the refrigerant to absorb heat more effectively. This results in better cooling and lower energy consumption.
Prevention of Freezing: In refrigeration units, proper airflow helps prevent the evaporator coils from freezing. When air isn’t circulated properly, the coils can get too cold, causing frost buildup that reduces the efficiency of the system.
Improved Air Distribution: The fan ensures that cool air is evenly distributed throughout the room or compartment, preventing uneven cooling and creating a more comfortable environment.
Energy Efficiency: A well-functioning evaporator fan reduces the need for additional cooling or more frequent compressor operation, which can save energy and lower operating costs.
Factors Affecting the Performance of an Evaporator Fan
While the evaporator fan plays a critical role in cooling efficiency, several factors can affect its performance:
Fan Blade Condition
The blades of the evaporator fan can wear out over time due to dust buildup, corrosion, or mechanical stress. Damaged blades can cause the fan to operate inefficiently, resulting in poor airflow and reduced cooling efficiency.
Motor Health
The motor that drives the evaporator fan can also experience wear and tear. Over time, it may lose power or fail entirely, which can result in the fan not operating correctly. A faulty motor often leads to noisy operation or complete fan failure.
Airflow Obstructions
If there are blockages in the airflow path—such as dust, debris, or ice buildup—it can restrict the fan’s ability to circulate air effectively. This can cause uneven cooling or even system breakdowns in extreme cases.
Temperature Regulation
The evaporator fan’s performance is closely tied to the temperature regulation system. If the thermostat or temperature sensors malfunction, the fan might continue running even when the space is sufficiently cooled, leading to unnecessary energy consumption.
Common Issues with Evaporator Fans and How to Troubleshoot Them
Understanding common issues with the evaporator fan can help you identify and resolve problems quickly. Here are some frequent issues:
Fan Not Running
If the evaporator fan isn’t running at all, it could be due to:
- A failed fan motor
- A blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker
- A faulty thermostat or temperature sensor
Noisy Fan Operation
A noisy fan may indicate:
- Loose or damaged fan blades
- A malfunctioning motor
- Debris caught in the fan housing
Reduced Airflow
If the fan is running but you notice reduced airflow, the issue could be:
- Blockages in the airflow path
- Dirty fan blades or coils
- An improperly sized fan for the unit
Freezing of Coils
Frozen coils can occur when:
- The fan is not circulating air properly
- The system is overcharged with refrigerant
- The evaporator coils are dirty or clogged
Intermittent Fan Operation
If the fan turns on and off intermittently, it might be due to:
- Faulty temperature sensors
- An issue with the thermostat
- An electrical problem in the fan circuit
Maintaining an Evaporator Fan
Proper maintenance of the evaporator fan is essential to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Here are some tips for keeping the fan in good condition:
Regular Cleaning: Clean the fan blades, motor, and coils regularly to prevent dust and debris buildup. This ensures the fan operates efficiently.
Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubrication to the fan motor to prevent wear and tear.
Check for Obstructions: Ensure there are no obstructions in the airflow path, such as ice buildup or debris.
Inspect for Wear: Regularly inspect the fan blades and motor for any signs of damage or wear, and replace components as needed.
Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on the fan’s operation and listen for unusual noises, as this can signal potential problems.
Conclusion
The evaporator fan is a key component in cooling systems, responsible for circulating air over the evaporator coils to facilitate heat transfer. By ensuring efficient air circulation, the fan helps optimize cooling performance, prevent system malfunctions, and reduce energy consumption. Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting are essential for ensuring that the fan continues to function effectively. Understanding how the evaporator fan works and how to care for it can help extend the lifespan of your cooling system and keep your environment comfortable year-round.
Related topics: