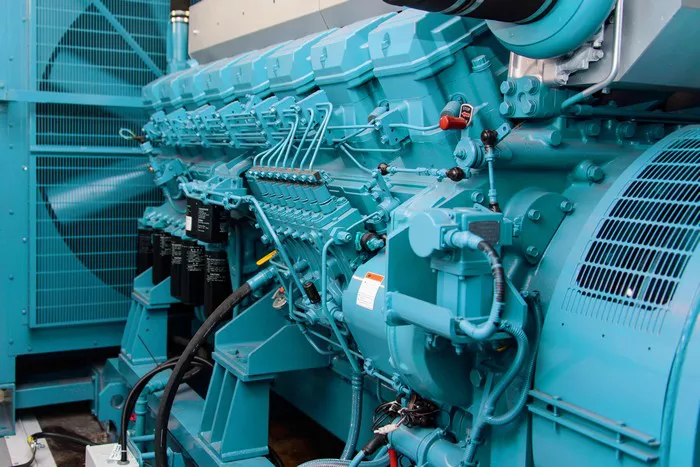
Diesel generators are widely used to provide backup power in various industries, businesses, and homes. They are a reliable and efficient power source, especially when electricity from the grid is unavailable. In this article, we will explore diesel generators in detail, their components, working principles, and applications. We will also highlight their advantages and maintenance requirements.
What is a Diesel Generator?
A diesel generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy from a diesel engine into electrical energy. Diesel generators are used as a source of backup power, providing electricity when the primary power source, usually from the grid, fails. The diesel engine runs on diesel fuel and powers an alternator to produce electricity.
Diesel generators are commonly used in locations where access to grid power is limited or unreliable. These generators are also used in areas where continuous power supply is critical, such as hospitals, data centers, and industries that require constant operations.
Types of Diesel Generators
There are several types of diesel generators available, each designed to meet specific power needs. Some of the most common types include:
Portable Diesel Generators: These are smaller, mobile generators that can be easily transported to different locations. They are typically used for temporary power needs, such as during outdoor events or on construction sites.
Stationary Diesel Generators: These generators are fixed in one location and are used for continuous or backup power generation. They are commonly found in businesses, hospitals, and industrial settings.
Silent Diesel Generators: As the name suggests, these generators are designed to run quietly, making them ideal for residential areas or locations where noise is a concern.
Prime Diesel Generators: These are designed to run continuously and are used in locations where there is no access to a main power grid. They are often used in remote locations, such as mining sites or offshore platforms.
How Does a Diesel Generator Work?
A diesel generator operates in a similar way to any other generator. The diesel engine burns fuel to create mechanical energy, which is transferred to an alternator. The alternator then converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy, which can be used to power electrical equipment.
Diesel Engine: The diesel engine is the heart of the generator. It works by burning diesel fuel in the engine’s combustion chamber. The engine’s pistons and crankshaft convert the energy from the burning fuel into rotational motion.
Alternator: The alternator is attached to the engine. As the engine runs, it turns the alternator’s rotor, generating alternating current (AC) electricity. The alternator’s job is to produce electrical power from the mechanical energy provided by the diesel engine.
Cooling and Exhaust Systems: Diesel engines produce heat during operation, which is why a cooling system is necessary. This system typically uses air or water to dissipate the heat. An exhaust system is also in place to safely vent the gases produced by the combustion process.
Control Panel: The control panel monitors and manages the operation of the diesel generator. It allows users to start, stop, and monitor the generator’s performance, ensuring it operates smoothly.
Key Components of a Diesel Generator
Understanding the key components of a diesel generator helps in appreciating its working mechanism and ensures effective maintenance. Here are the primary parts of a diesel generator:
1. Diesel Engine
The engine is responsible for generating mechanical power by burning diesel fuel. It is one of the most important components, and its efficiency plays a significant role in the overall performance of the generator.
2. Alternator
The alternator produces electrical power. It consists of a rotor and a stator. The rotor is connected to the diesel engine and generates a rotating magnetic field. The stator, which surrounds the rotor, converts this magnetic field into electrical current.
3. Cooling System
The cooling system ensures that the diesel engine does not overheat during operation. It typically includes a radiator, water pump, and coolant.
4. Fuel System
The fuel system supplies diesel to the engine. It includes components like the fuel tank, fuel pump, and fuel filter.
5. Lubrication System
The lubrication system reduces friction between moving parts in the engine. It includes the oil pump, oil filter, and oil reservoir.
6. Control Panel
The control panel provides information about the generator’s operational status, such as fuel levels, voltage output, and engine temperature. It is also used to start and stop the generator.
7. Battery
The battery is used to start the generator. It provides the initial electrical charge to power the starter motor.
Advantages of Diesel Generators
Diesel generators offer several advantages, making them a preferred choice for backup power. Below are the key benefits:
1. Fuel Efficiency
Diesel engines are highly fuel-efficient, meaning they can generate more power per unit of fuel compared to other types of engines. This makes them an economical choice for long-term use.
2. Durability and Reliability
Diesel generators are known for their durability. Diesel engines typically have a longer lifespan than gasoline engines due to their robust design and fewer moving parts.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Although diesel generators may have a higher initial cost, they are cheaper to maintain and operate over time due to their fuel efficiency and long lifespan.
4. Easy Maintenance
Diesel engines are relatively easy to maintain. Regular maintenance, such as changing the oil and checking fuel filters, can ensure the generator operates efficiently for years.
5. Power Output
Diesel generators can provide high power output, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They can power large machinery and equipment in industrial settings.
6. Environmentally Friendly
Modern diesel engines are designed to minimize emissions, making them a more environmentally friendly option compared to older models.
Applications of Diesel Generators
Diesel generators are used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility. Some common uses include:
1. Backup Power Supply
One of the primary applications of diesel generators is as a backup power source during power outages. This is especially important in critical sectors like healthcare, where uninterrupted power is vital for medical equipment and patient care.
2. Construction Sites
Construction sites often rely on diesel generators for power, as they are usually located far from the electrical grid. Diesel generators provide the necessary power to run tools and equipment.
3. Telecommunications
Telecommunication companies use diesel generators to ensure continuous operation of their networks. Diesel-powered generators are essential for maintaining communication services during emergencies or power disruptions.
4. Industrial Operations
Industries that rely on heavy machinery require reliable power sources. Diesel generators provide a steady supply of electricity for manufacturing processes, especially in remote locations.
5. Events and Festivals
Diesel generators are commonly used to power events and festivals, providing electricity for lighting, sound systems, and food vendors. They are portable and can be moved to different locations as needed.
Diesel Generator Efficiency and Performance
The performance of a diesel generator depends on several factors, including the engine size, load capacity, and maintenance practices. It is essential to choose a generator that meets the power needs of the intended application.
1. Load Management
When operating a diesel generator, it is important to manage the load efficiently. Overloading the generator can cause it to overheat and reduce its lifespan. Proper load balancing ensures optimal performance and prevents unnecessary strain on the system.
2. Fuel Quality
The quality of diesel fuel affects the performance of the engine. Low-quality fuel can lead to engine damage and decreased fuel efficiency. It is important to use clean, high-quality diesel to maintain the generator’s performance.
3. Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the diesel generator operates at peak efficiency. This includes changing the oil, inspecting the cooling system, and checking fuel filters. A well-maintained generator performs better and lasts longer.
Diesel Generator Maintenance Tips
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of a diesel generator, it is essential to follow a regular maintenance schedule. Some important maintenance tips include:
Change the Oil: Regular oil changes are essential for keeping the engine running smoothly. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for oil change intervals.
Inspect the Fuel System: Check for fuel leaks, and clean or replace fuel filters as needed.
Check the Battery: Inspect the battery regularly to ensure it is charged and in good condition.
Test the Generator: Run the generator regularly to ensure it is functioning properly. This helps prevent issues when it is needed most.
Clean the Cooling System: Keep the cooling system clean and ensure it is free of debris to prevent overheating.
Conclusion
Diesel generators are reliable and efficient sources of backup power. They are used in a variety of applications, from industrial operations to residential areas, where they provide essential power during outages or in remote locations. Diesel engines are durable, fuel-efficient, and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for powering electrical equipment. Regular maintenance and proper operation are crucial to ensure the longevity and reliability of diesel generators.
Related topics: