Transformers are critical components in electrical power systems, ensuring efficient voltage conversion and power distribution. To guarantee their reliability and performance, various tests are conducted during manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. These tests help identify potential issues, verify compliance with standards, and ensure safe operation. This article provides a detailed overview of the key transformer tests, their purposes, and methodologies.
Types of Transformer Tests
Transformer tests can be broadly categorized into three groups: routine tests, type tests, and special tests. Each category serves a specific purpose in evaluating transformer performance and safety.
Routine Tests
Routine tests are mandatory tests performed on every transformer to ensure basic functionality and quality. These tests confirm that the transformer meets standard specifications.
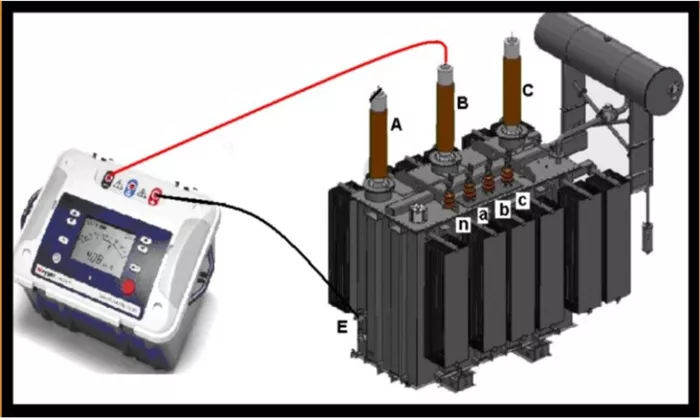
Winding Resistance Test
The winding resistance test measures the DC resistance of transformer windings to detect issues such as loose connections, broken strands, or high contact resistance. This test helps identify potential overheating problems and ensures the windings are correctly manufactured. The measurement is typically done using a micro-ohmmeter or a Wheatstone bridge.
Turns Ratio Test
The turns ratio test verifies the voltage ratio between primary and secondary windings. A significant deviation from the expected ratio may indicate shorted turns or incorrect winding connections. This test is crucial for ensuring proper voltage transformation and is performed using a turns ratio tester.
Insulation Resistance Test
Insulation resistance testing evaluates the condition of the transformer’s insulation system. A megohmmeter applies a high DC voltage to measure resistance between windings and ground. Low insulation resistance may indicate moisture ingress, contamination, or insulation degradation.
Polarity and Phase Relation Test
This test confirms the correct polarity and phase relationship in multi-winding transformers. Proper polarity ensures that transformers operate in parallel without causing circulating currents. The test is conducted using a voltage comparison method or a phase angle meter.
Type Tests
Type tests are performed on a representative sample of transformers to validate design and construction. These tests are not repeated unless design changes occur.
Temperature Rise Test
The temperature rise test assesses the transformer’s ability to dissipate heat under rated load conditions. Excessive temperature rise can lead to insulation failure. The test involves applying full load current while monitoring temperature changes in windings and oil.
Lightning Impulse Test
This test evaluates the transformer’s ability to withstand lightning-induced voltage surges. A high-voltage impulse generator applies standardized lightning waveforms to the windings. The test ensures that the insulation can handle transient overvoltages without breakdown.
Short Circuit Test
The short circuit test checks the mechanical and thermal strength of the transformer under fault conditions. A high current is passed through the windings to simulate a short circuit. The test verifies that the transformer can endure electromagnetic forces without damage.
Special Tests
Special tests are conducted based on specific requirements or unusual operating conditions. These tests provide additional insights into transformer performance.
Dielectric Dissipation Factor Test
The dielectric dissipation factor (tan delta) test measures insulation quality by assessing energy losses in the dielectric material. High tan delta values indicate insulation aging or contamination. This test is useful for diagnosing insulation health in power transformers.
Partial Discharge Test
Partial discharge testing detects localized electrical discharges within insulation. These discharges can erode insulation over time, leading to failure. The test uses high-frequency sensors to identify partial discharge activity.
Sweep Frequency Response Analysis (SFRA)
SFRA assesses mechanical integrity by analyzing the frequency response of transformer windings. Changes in the response curve may indicate winding deformation, core movement, or loose connections. This test is particularly useful after transportation or short-circuit events.
Importance of Transformer Testing
Transformer testing is essential for ensuring operational reliability, preventing failures, and extending equipment lifespan. Regular testing helps detect early signs of deterioration, allowing timely maintenance and avoiding costly downtime. Additionally, compliance with international standards such as IEC, IEEE, and ANSI ensures safety and performance consistency.
Conclusion
Transformer tests play a vital role in maintaining power system stability. From routine checks to specialized diagnostics, each test provides valuable insights into transformer health. By understanding these tests, engineers can make informed decisions regarding maintenance, repair, and replacement, ultimately enhancing grid reliability. Proper testing protocols contribute to safer, more efficient electrical networks, supporting uninterrupted power supply for industries and communities.
Related Topics: